Secure a Web App Using Google
Enable SSO and Granular Access Control For A Header-Based Web App with Google
Preview
In this tutorial, we will use the Datawiza Access Proxy (DAP) to enable SSO and granular access control for a header-based web App. The IdP we will use is Google. We will use DAP's side deployment mode, which means DAP and this app are running on the same server.
- We will use a built-in web application as the header-based web App.
- The DAP will run on
localhost:9772, which means the traffic to the app will reach DAP (running on port 9772) first and then be proxied to the web application. - We will provide the docker images for the DAP.
Part I: Google Configuration
You will need to register a credential in Google API Console and get the following 2 values for this credential:
- Client ID
- Client Secret
These values will later be used to set up Datawiza Access Proxy in Datawiza Cloud Management Console. Please follow IdP Configuration Guide: Google instructions on how to get those keys/values.
Part II: Create Application on Datawiza Cloud Management Console (DCMC)
You need to create an application and generate a keypair of (PROVISIONING_KEY, PROVISIONING_SECRET) for this app on the DCMC.
Please follow Step2 : Datawiza Cloud Management Console to configure.
Part III: Run DAP
You can use either Docker or Kubernetes to run DAP. The following is an example docker-compose.yml file. You may need to login to our container registry to download the images of DAP and the header-based app. See Step3 : Configure DAP and SSO Integration for more details or Deploy DAP with Kubernetes for Kubernetes-specific instructions.
version: '3'
services:
datawiza-access-proxy:
image: registry.gitlab.com/datawiza/access-proxy
container_name: datawiza-access-proxy
restart: always
ports:
- "9772:9772"
environment:
PROVISIONING_KEY: #############################
PROVISIONING_SECRET: #############################
After executing docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml up, the header-based app should have SSO enabled with Google. Open a browser and type in http://localhost:9772/. You should see the Google login page as follows. 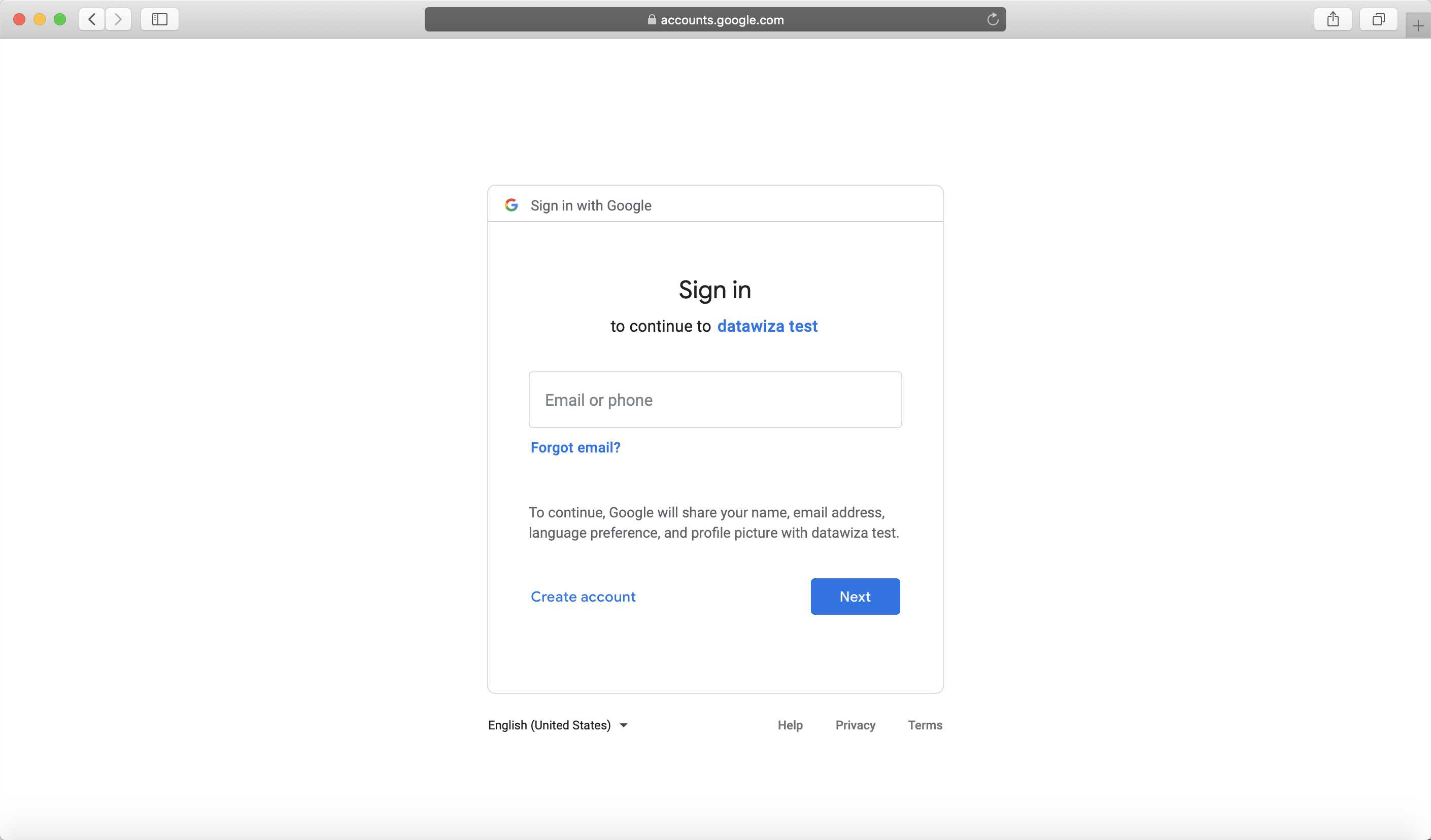
Part IV: Pass User Attributes to the Header-Based App
The DAP gets user attributes from the IdP and can pass the user attributes to the application via header or cookie.
Please follow the instructions of Step4 : Pass User Attributes to pass the user attributes to the header-based app.
After successfully configuring the user attributes, you should see the green check sign for first three user attributes as follows. 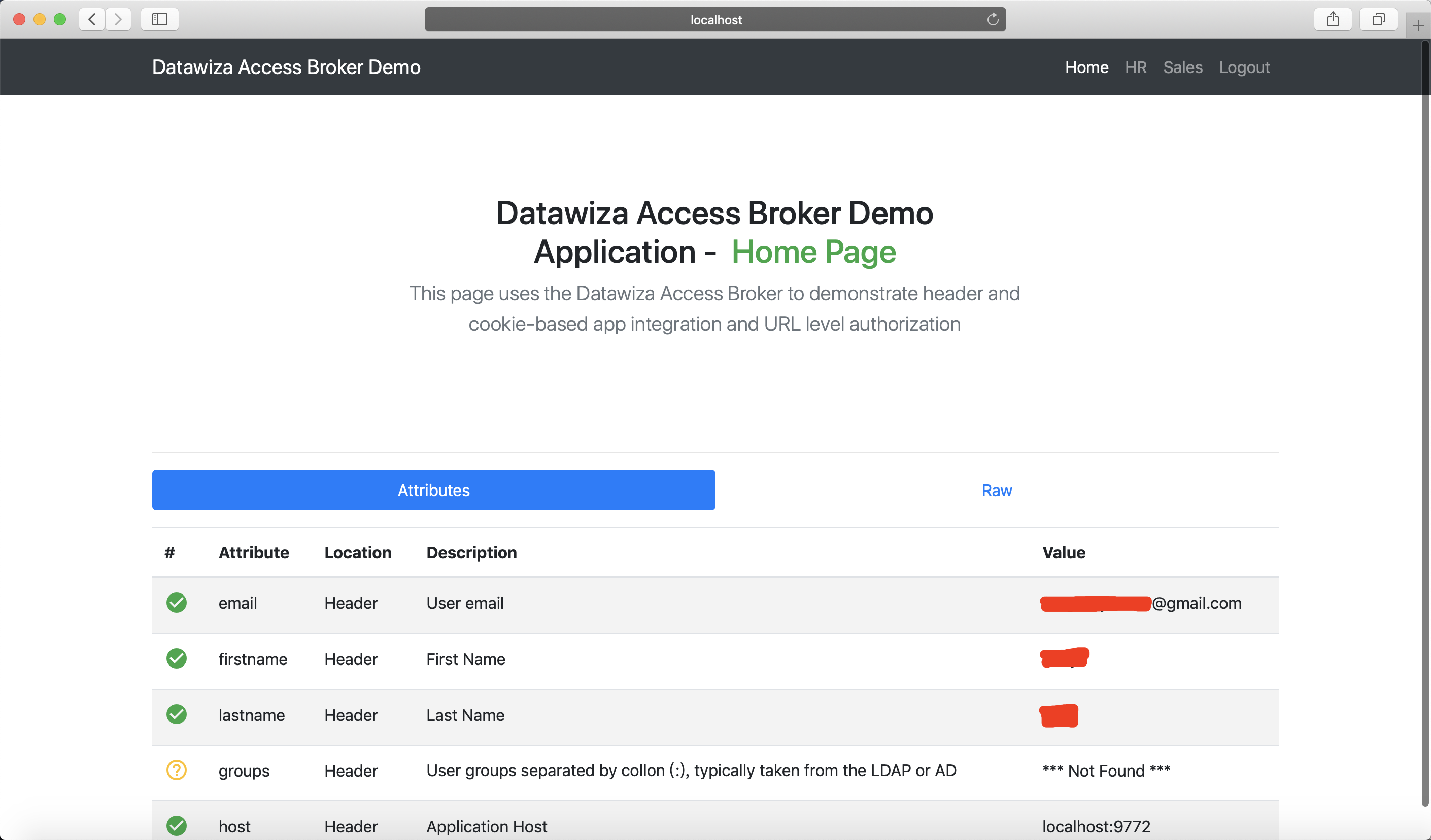
Part V: Achieve Granular Access Control
You can configure access control to an application based on user's attributes (e.g., given name, family name) and other metadata of a request (e.g., URL, IP, http method, access time).
Please reference Step5 : Achieve Granular Access Control for detailed instructions on how to set up access rules.
A Rule Example
- Create the following two rules: Because Google social account doesn't have group or role, we use first name here as example:
hr pathcan only be accessed by the user whose first name isWest.sales pathcan only be accessed by the user whose first name isJohn.
- Verify that the user can only access
hrpage in the header-based app, but cannot accesssalespage. Trying to access the header-based application onlocalhost:9772in your browser, you should get something similar to the following screenshots.http://localhost:9772/hr: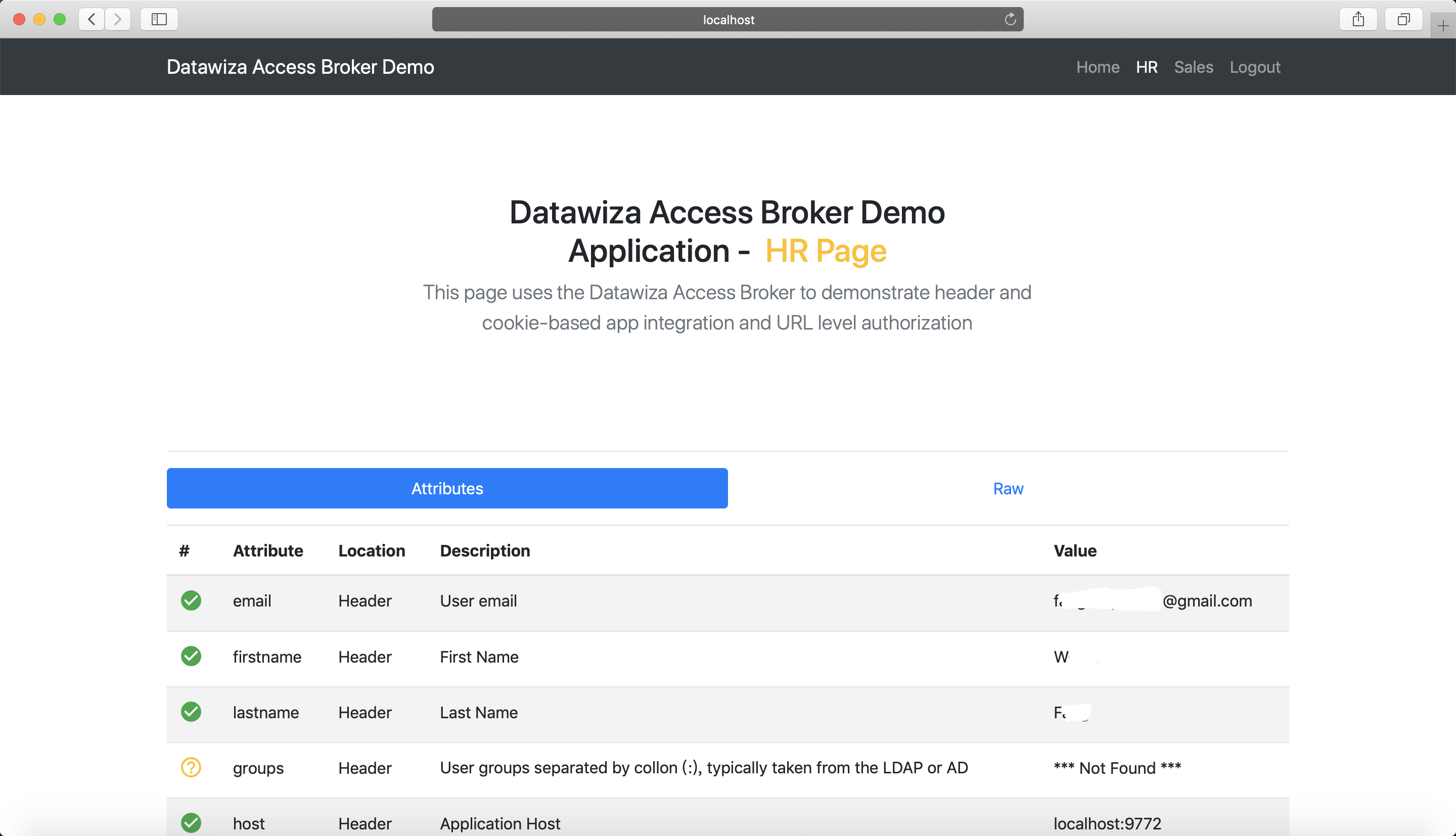
http://localhost:9772/sales: